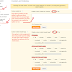
Step 1: Go to Settings > Search Preferences
Web site owners use the /robots.txt file to give instructions regarding which links of the site are to be searched (or indexed) about their site to web robots (also known as Web Wanderers, Crawlers, or Spiders; they are programs that traverse the Web automatically. Search engines such as Google use them to index the web content); this is called The Robots Exclusion Protocol. In short Search engines are robots.
Step 2: What to put in robots.txt content?
1. To exclude all robots from the entire server
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
The "User-agent: *" means this section applies to all robots.
2. To allow all robots complete access
User-agent: *
Disallow:
(or just create an empty "/robots.txt" file, or don't use one at all)
3. To exclude a single robot
User-agent: BadBot
Disallow: /
4. To allow a single robot
User-agent: Google
Disallow:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
5. Disallow particular post by using robots.txt file
User-agent: *
Disallow: /yyyy/mm/post-url.html
Here yyyy and mm refers to the publishing year and month of the post respectively. For example, if we have published a post in year 2014 in the month of December then we have to use the below format.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /2015/12/post-url.html
One thing you should keep in mind that it is case sensitive. So the best method is to copy the exact URL, remove the Blogger address and paste here for best results. Otherwise, it will create trouble for your blog.
6. Disallow Particular Page(s) by using robots.txt file
This method is same as to disallow the crawling of the particular post. You just need to copy the URL of the particular page(s) you want to block, remove the domain name and use in your robots.txt file like the below code:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /p/page-url1.html
Disallow: /p/page-url2.html
Disallow: /p/page-url3.html
This is normally used to prevent the "Privacy Policy", "Terms & Conditions" and "Disclaimer" pages from being crawled by Googlebot and other crawlers and spiders.
Custom Robots Header Tags
Its scope is narrower as compared to the above option.
As far as robot header tags are concerned, all pages on a blogger blog are classified into three categories:
Home Page – This category includes a single page, the home page of your blog.
Archive and Search pages – Archive pages are those which list multiple blog posts (or snippets) on a single web page. These are the page accessed by clicking the ‘Older’and ‘Newer’ links at the bottom of the home page and all pages reached by clicking these links, or the pages accessed by clicking the Year or Month links in the blog archives.
Search pages are those which open on searching in a blogger blog. These pages also show multiple blog posts on a single page.
Pages and Posts – These are the blog post pages or standalone blogger pages. These pages show only a single blog post and the associated comments.
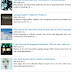
It does not provide you the opportunity to write your codes instead it is confined to the following options (See picture above), along with their brief definitions:-
- all: No restrictions are placed on the robots. They are allowed to crawl, index and serve content. This is the default value.
- noindex: The page shouldn’t be indexed i.e. it shouldn’t be shown in search results.
- nofollow: All links on the page containing this directive will be treated as nofollow. The page will be indexed but the linked pages will not be crawled. Note that if there is another web page somewhere on the internet having links to those pages marked as nofollow by you, then those pages will be crawled. The nofollow directive simply states that ‘Do not index the linked pages because I have linked to them. But, if someone else has linked to them and has not marked them as nofollow, then you are free to index them’.
- none: Equivalent to both "noindex" and "nofollow".
- noarchive: Google caches certain web pages and shows a link to the cached pages in search results. If noarchive tag is specified, then the cached link will not be shown in search results.
- nosnippet: Along with links to webpages, Google search results also shows a text snippet to give the searcher an idea of the contents of that page. If nosnippet is set, then text snippets will not be shown for that page in search results.
- noodp: The Open Directory Project (dmoz.org) is a human created directory of websites and webpages. The human editors also add descriptions for these webpages. Sometimes, Google uses these descriptions (and other information) to improve the text snippets or other information shown in search results. If the noodp tag is set, Google will not use metadata from ODP.
- notranslate: If the language of the user is different from the language of the webpage, Google shows a link in its search results for translating that page. If notranslate is set, then such links won’t be shown.
- noimageindex: If set, the images on that page will not be indexed. This is similar to nofollow tag. If the same image is present on some other page, then that image may be indexed.
- unavailable_after: The webpage will not be shown in search results after the specified date and time.
If the feature is turned on (e.g., you’ve selected Yes), then you will see a similar interface in the "Post Settings" section of the Post Editor.


.png)